Invoicing in Germany - what you need to know
Whether you’re planning to expand into the German market or are already trading with German partners, it is really important to fully understand local invoicing rules. At Eurofiscalis, our German office regularly assists businesses with these complexities, and we know that non-compliance can lead to delays, penalties, or tax complications.
- Published on :
- Reading time : 13 min
Invoicing in Germany – quick introduction
Germany is known for strict invoicing requirements for both traditional and electronic invoices. As you may know, any non-compliance will lead your business to delays, penalties, or tax complications.
Nowadays, there are a lot of changes in the invoicing field. The EU pushes forward with its fully digital transformation, at the same time Germany is taking big steps to modernize its invoicing landscape.
German invoicing news in 2025-2028 – what’s changing?
From January 1, 2025:
E-invoicing has already been mandatory for public sector (B2G) transactions since November 27, 2020, and starting January 1, 2025, it will become a legal obligation for all businesses to receive electronic invoices in B2B transactions.
From 2027:
Issuing e-invoices will also become mandatory, depending on business size → in 2027 for>€800,000
From 2028:
All German taxpayers will have to issue electronic invoices.

Legal requirements for invoicing in Germany
It is important to clarify the German legal foundation for every invoice – paper, PDF or electronic format. Complying with these requirements is not just about good bookkeeping – it’s an essential part for deducting input VAT and avoiding any trouble with the German tax authorities.
What are the requirements for invoicing in Germany?
If you want to ensure an invoice is legally valid in Germany (according to § 14 UStG – German VAT Act), it is mandatory to include:
- Supplier’s and customer’s information such as full name and address
- Invoice number – unique, sequential
- The date of issue
- Description of goods or services supplied
- Net amount
- VAT rate(s)
- The total gross amount
- Supplier’s VAT ID number
- Customer’s VAT ID number – if intra-community supply
- Reference to tax exemptions or reverse charge – if applicable
You can book a free consultation with our VAT experts in time that is suitable for you!
How to invoice in Germany? - issuance and storage regulations
Based on the German VAT law, invoices must:
- Invoices must be issued within six months of the supply of goods or services – according to Section 14 of the UStG.
- All invoices must be archived for ten years in a readable and unaltered format – based on § 147 AO (German Fiscal Code).
- It doesn’t matter whether it is a paper or electronic invoices – all are acceptable provided authenticity, integrity, and when readability are guaranteed. However it will not be the case for B2B transactions from 2028 onwards (and for receiving e-invoices from 2025).
Transition to e-invoicing in Germany
As it was written at the beginning of the article – Germany is not just in the process of adopting e-invoicing, but it’s fully transforming how businesses manage VAT compliance.
Definition and benefits of e-invoicing in Germany
E-invoicing refers to invoices that are created, transmitted, and processed entirely in a digital format.
There is a difference between electronic invoices and PDF format. E-invoices are more than sending PDFs. True e-invoices are fully structured data files that can be automatically read by business systems.
What are the benefits for businesses?
- Lower processing costs
- Faster payment cycles
- Fewer errors
- Better tax reporting and audit readiness
Regulatory framework for electronic invoices
Germany is aligning with EU Directive 2014/55/EU, which mandates e-invoicing for public procurement. However, national laws like the E-Rechnungsgesetz and the E-Rechnungsverordnung define how and when e-invoicing becomes mandatory.
The Wachstumschancengesetz (Growth Opportunities Act) is the main piece of legislation requiring B2B e-invoicing, whilst the E-Rechnungsgesetz mostly regulates B2G. Since the Wachstumschancengesetz is essential to the 2025–2028 revisions, it could be helpful to particularly address it here.
You can book a free consultation with our VAT experts in time that is suitable for you!
- Is e-invoicing mandatory in Germany 2025?
Yes, from January 1, 2025, all businesses in Germany must be able to receive structured e-invoices.
Mandatory e-invoicing for B2G transactions in Germany
Application and scope
Since November 27, 2020 ⇒ e-invoicing has been mandatory for B2G (business-to-government) transactions in Germany. Any German business invoicing a federal or state authority must submit a structured e-invoice (paper and PDFs are no longer accepted).
- What is the scope of e-invoicing in Germany?
It all started with B2G but is now expanding to cover all B2B transactions.
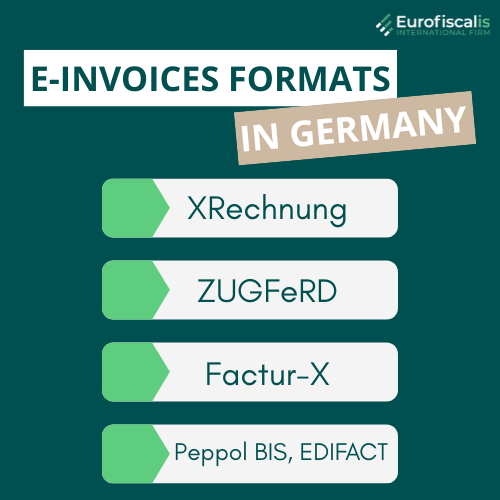
Formats for German e-invoices
It is required by the German government to use a specific format for e-invoices, which is:
- XRechnung – the standard German format, which is fully compliant with EN 16931 – the EU e-invoicing standard.
Public organisations are able to use centralized German platforms such as ZRE (federal) or OZG-RE (state-level) to receive or submit invoices.
Sources: ZRE
You can book a free consultation with our VAT experts in time that is suitable for you!
Implementation of B2B e-invoicing in Germany – timelines
To answer the question like “Is e-invoicing mandatory in Germany 2025?” please look at the table.
Mandatory e-invoicing for B2B transactions is happening in phases:
| Timeline | Thresholds |
|---|---|
| January 1, 2025 | All businesses must be able to receive e-invoices |
| January 1, 2027 | Issuance becomes mandatory for businesses with annual turnover > €800,000 |
| January 1, 2028 | All B2B invoicing must be electronic (regardless of turnover) |
B2B - who is affected?
taxable supplies and services between businesses (doesn’t matter whether the business is operated as a primary or secondary activity)
require that both the supplier and the recipient be resident in Germany
German thresholds for 2025
Germany has raised the Intrastat reporting thresholds for 2025
- For its intra-EU imports: increase from EUR 800,000 to EUR 3,000,000 annually.
- For its intra-EU exports: increase from EUR 500,000 to EUR 1,000,000 annually.
The amendment to the Act on Statistics of Foreign Trade was approved by the Bundesrat on February 14th with effective from Jan 1, 2025, going forward.
Check updated EU Intrastat thresholds for 2025:
Legal basis for German electronic invoices
All the legal basis of German laws (including E-Rechnungsgesetz for B2G and Wachstumschancengesetz for B2B) and is supported by the EU’s directives 2014/55/EU and the broader goals of VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA).
German technical and formats standards for e-invoicing
As it was written before, while in Germany XRechnung is directly compliant, ZUGFeRD and Factur-X and other formats must meet the EN 16931 standard.
- XRechnung – is mandatory for B2G, however also accepted in B2B
- ZUGFeRD – is a hybrid format which is combining both human-readable PDF with machine-readable XML
- Factur-X – is comparable to ZUGFeRD, but is more common in cross-border scenarios
- Peppol BIS, EDIFACT – are supported only if compliant with EN 16931, the Peppol is not mandatory but really useful in cross-border invoicing within the EU
Select the format
By what criteria should you select the format? – ask yourself these question:
- If it is a domestic or cross-border?
- What are the requirements of your trading partners?
- What is compatibility with your accounting or ERP systems?
E-invoicing process for German B2B transactions
How e-invoicing works in practice?
E-invoice – generate and transmit
All of the invoices must be created by ERP systems or invoicing software which are compliant with your business. Accepted transmission methods especially include:
- Secured email with structured attachments
- EDI – Electronic Data Interchange
- Peppol network
E-invoice - receipt and process
The recipients must be ready to receive and be able to process German e-invoices in structured formats (detailed above) from January 2025.
E-invoice – archive obligations
E-invoices must be:
- Stored in their original format for 10 years
- Archived in a way that ensures data integrity and readability
It is really important in case of an audit of any tax audits or problems.
What is the difference between B2B and B2G e-invoicing in Germany?
| Characteristic | B2G | B2B |
|---|---|---|
| Oversight | Public procurement offices | Federal Ministry of Finance |
| Platform | ZRE, OZG-RE | No central platform – private providers |
| Format | Strict XRechnung | Flexible (if EN 16931-compliant) |
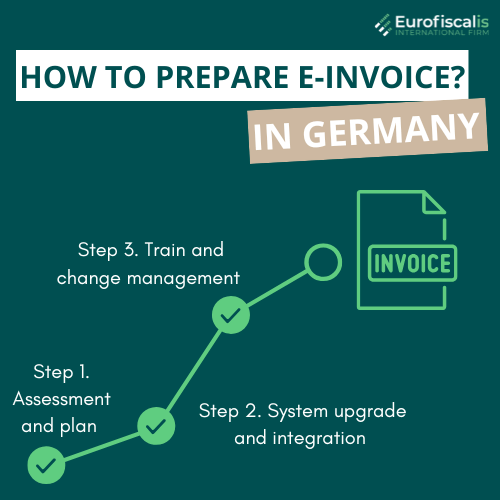
How to prepare for a switch to e-invoicing in Germany?
To stay compliant and updated your business should remember:
Step 1. Assessment and plan – map your current invoicing processes, identify gaps and compare them to any official future legal requirements
Step 2. System upgrade and integration – upgrading your software in order to support structured invoice formats. This will enable secure and compatible channels for transmission
Step 3. Train and change management – when it comes to changes it is really important to keep up with educating your own finance teams. They must be updated on any upcoming internal procedures and controls
VAT and invoicing in Germany
- Do I charge VAT on invoices to Germany?
- if your business is VAT-registered in Germany and you're selling to another German business or private customer
- if you're a foreign business and the reverse charge applies (as it is with B2B intra-EU supplies)
Remember! Be sure to include the correct wording on your invoice.
Need expert help with invoicing and VAT in Germany?
Our German office provides a range of specialized services to ensure your business stays compliant and efficient:
Zosia is a marketing specialist in Eurofiscalis, a company with a well-established position in the field of cross-border VAT compliance. Simultaneously, Zosia continues her academic development as a master’s student in Finance and Accounting, which enables her to stay up-to-date with evolving tax regulations.
Combining her knowledge of marketing with a deep understanding of finance and taxes, creates precise, substantive, and easily accessible content. Her mission is to educate in understanding the complexities of taxation related to doing business in international markets.
With her commitment, Zosia translates complex tax issues into clear language, providing valuable information that genuinely helps companies in their development and international expansion. She aims for tax information to be not only understandable but, above all, helpful in making business decisions.