How to import goods to Norway? VAT rules
Considering import goods to Norway? The question of what can be imported is paramount, and navigating Norway’s specific regulations requires a nuanced understanding. Unlike EU member states, Norway operates under its own set of rules, making it crucial to understand the specific requirements for a smooth and compliant import process. This article, brought to you by Eurofiscalis, provides a comprehensive breakdown of essential VAT rules, customs procedures, and compliance steps. Whether you’re a seasoned importer or new to the Norwegian market, understanding these guidelines is vital to avoid penalties and ensure your goods clear customs efficiently.
- Published on :
- Reading time : 12 min
Understanding the basics of importing to Norway
Is Norway part of the EU Customs Union?
No, Norway is not part of the EU Customs Union. It is a member of the European Economic Area (EEA), meaning it follows certain EU trade regulations but has its own customs and VAT system.
Importing goods into Norway requires compliance with Norwegian customs procedures and VAT regulations. Unlike EU member states, Norwegian import procedures involve customs clearance and the payment of import duties and VAT at the time of importation, unless deferred payment schemes apply.
Import goods to Norway - key authorities involved
The main authorities responsible for regulating imports into Norway are:
- Norwegian Customs (Toll.no) oversees customs declarations, duties, and import controls.
- Norwegian Tax Administration (Skatteetaten) handles VAT registration, reporting, and compliance.
Businesses must interact with these entities to ensure proper documentation, tax payments, and legal compliance when importing goods.
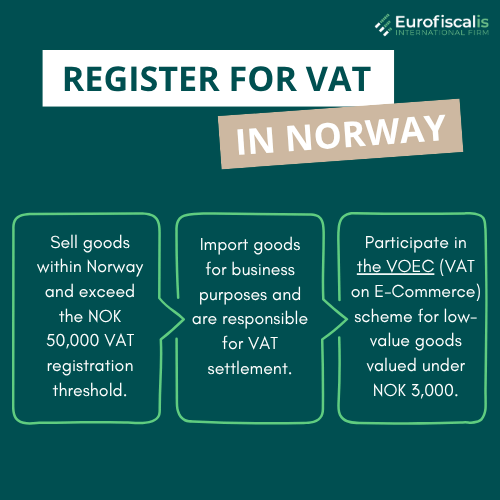
Who needs to register for VAT in Norway?
Businesses importing goods into Norway may need to register for VAT if they:
- Sell goods within Norway and exceed the NOK 50,000 VAT registration threshold.
- Import goods for business purposes and are responsible for VAT settlement.
- Participate in the VOEC (VAT on E-Commerce) scheme for low-value goods valued under NOK 3,000.
A short step-by-step guide
- Check product restrictions and required permits.
- Determine VAT and duty obligations.
- Declare goods at customs.
- Pay applicable taxes or use deferred payment options.
- Ensure compliance with VAT reporting rules.
Prohibited and restricted products in Norway
There may be restrictions or prohibitions on the importation of certain commodities. To import certain items into Norway, the Norwegian government might need paperwork or permits. Before trading such products, make sure you are following the rules set forth by the relevant Norwegian government.
Restricted Goods | Competent Authority | Alcohol and Tobacco | Norwegian Tax Administration, Norwegian Directorate of Health
|
|---|---|
Foodstuffs, plants, seeds, animals | Norwegian Food Safety Authority |
Waste, endangered species (CITES) | Norwegian Environment Agency |
Medicines | Norwegian Medicines Agency |
Explosives, fireworks | Directorate for Civil Protection and Emergency Planning |
Weapons and ammunition | Norwegian Police |
Cultural monuments, antiques | Norwegian Directorate for Cultural Heritage |
Norwegian excise taxes

Certain goods are subject to excise taxes. The tariffs are determined annually by the Norwegian government. There are differences in excise duty rates and calculation methods.
If the items you are importing are subject to an excise duty, you need to get familiar with the rules governing this excise duty.
- non-alcoholic beverages
- alcoholic beverages
- chocolate and sugar products
- sugar
- tobacco products
- one-off tax on vehicles
Possibility of reduced duty or duty relief
Norway has free trade agreements with several countries. This means that goods subject to duty may be entitled to a reduced customs duty rate or duty-free status if the goods are covered by a free trade agreement. It is mainly foodstuffs and textiles that are subject to customs duty when imported into Norway.
Free trade agreements do not apply to VAT or any excise duties.
- importing clothing
- importing food (foodstuffs)
- Duty-free status or reduced duties on imports

You can book a free consultation with our VAT experts in time that is suitable for you!
Customs procedures for importing to Norway
Declaring goods at customs in Norway
All goods entering Norway must be declared to Norwegian Customs. The declaration process includes:
- Providing accurate product descriptions, HS codes, and values.
- Submitting necessary documentation, including invoices, transport documents, and certificates of origin.
- Using a customs broker or digital declaration system for a smoother process.
Proper customs declaration is crucial for avoiding penalties and ensuring that the correct amount of VAT and customs duties are paid. Norwegian authorities require businesses to use electronic declaration systems, and incorrect reporting can lead to audits and delays.
Provisional and final declarations
Businesses can submit a provisional declaration if exact details are unavailable at the time of import.
A final declaration must be submitted later to confirm the details and ensure proper VAT and duty calculations.
This system helps businesses manage imports efficiently while ensuring compliance.
Norwegian customs warehouses
Businesses can hold imported products in Norwegian customs warehouses without having to pay import VAT and charges until the commodities are released for free circulation.
Significant cash flow benefits may result from this, particularly for businesses that handle high import volumes or reexport commodities.
Norway’s customs warehouse types:
⇒ Public customs warehouses:
Available for use by multiple importers, typically managed by third-party logistics providers.
⇒ Private customs warehouses:
Reserved for a single business that imports and stores its own goods under customs supervision.

There are four main kinds of customs warehouses in Norway:
- Type A customs warehouse (general warehouse)
- Type B customs warehouse (central warehouse)
- Type C customs warehouse (duty-free sales at airports)
- Type D customs warehouse (processing warehouse)
A customs warehouse is beneficial to companies that:
– Bring in a lot of merchandise and distribute it gradually.
– VAT and customs charges must be postponed until after the products are sold or used.
– Avoid paying Norwegian import VAT by storing items for future export.
– Before releasing products onto the Norwegian market, allow extra time for quality assurance, processing, or repackaging.
Reporting and application requirements:
Businesses must get permission from Norwegian Customs (Toll.no) in order to operate or use a customs warehouse in Norway.
The procedure entails:
1. submitting an application that includes information about the type, location, and intended use of the warehouse.
2. keeping thorough records of every item being stored, including its transportation, length of storage, and eventual clearance.
3. observing the regular audits carried out by Norwegian Customs to guarantee accurate reporting and compliance with rules.
Applying for a TRK – Customs ID number
Importers must obtain a TRK number (Tollkreditt) to pay customs duties and VAT efficiently. This simplifies transactions with Norwegian Customs. Businesses importing frequently benefit from a customs credit account, which allows deferred payment of customs duties and VAT, improving cash flow management.
Apply for a TRK number:
1. If a person does not have a Norwegian personal ID number or D number, they must apply for a TRK number. D number is a short-term identification number.
2. Those who have a Norwegian D number or personal ID number but have either recently moved abroad or have reported leaving Norway.
3. Businesses that are not listed in the Norwegian Business Register with a Norwegian organisation number.
How do you apply?
- In Altinn without using email (the paper forms are no longer available)
- Use ID-Porten to access Altinn as usual if you have a Norwegian Social Security number or D Number and wish to apply on behalf of another business.
Remember to include the following information in your application:
1. Private citizens must include:
– A copy of an official document, such a passport.
– Consignment note, invoice, or clearance paperwork for the disputed goods.
2. Businesses need to include the following:
– Invoice or consignment note that includes the enterprise’s nation of origin, the consignment’s correct ID number, TIN/TNI/EORI/UEI or DUNS, etc.
– You must include a document verifying the enterprise’s ID number if it isn’t mentioned on the invoice or consignment note. This can be a certificate of registration with the foreign organisation number from a foreign public register of businesses.
You can book a free consultation with our VAT experts in time that is suitable for you!
Import goods to Norway - VAT rules
When and how to report VAT on imports?
Deferred import VAT in Norway, also known as the import reverse charge mechanism, was introduced on January 1, 2017, fundamentally changing how this tax is accounted for. Previously, importers were required to pay the due import VAT directly to the Norwegian Customs Service (Tolletaten) at the time of customs clearance for imported goods. Currently, as informed by the Norwegian Tax Administration (Skatteetaten), the obligation to calculate and declare import VAT lies with the importer and is fulfilled through their periodic VAT return (MVA-melding).
The deferred import VAT system can be utilized by entities registered in the Merverdiavgiftsregisteret (the Norwegian VAT register) – simply put, those who possess a Norwegian VAT number. Importantly, there’s no need to apply for the deferred import VAT procedure; every taxpayer who registers for VAT in Norway automatically acquires this capability.
The basis for calculating import VAT in Norway is the customs value of the goods, increased by any customs duties and other fees, according to the data from the customs declaration available in the Altinn system.
The declared output import VAT is simultaneously deducted as input VAT within the same VAT return (provided the importer has the right to deduct it). This effectively defers the payment of import VAT and, as a result, improves the importer’s cash flow.
Taxes and duties on imported goods in Norway
In Norway, customs taxes, VAT, and possible excise taxes apply to all imported items. The kind and value of the items determine how much. Important things to think about are:
- Customs duties are levied on certain commodity categories, such textiles and food.
- Import VAT usually 25%, this tax is determined by adding any duties to the customs value.
- Excise duties extra levies on particular products, such cigarettes and alcohol.
In order to calculate the appropriate tariffs and taxes, importers must make sure that their items are properly classified. There may be penalties and delays for underreporting or misclassification.
Import VAT calculation
VAT on imports is calculated based on:
- Customs value (CIF) – including cost, insurance, and freight.
- Customs duties and other taxes.
- Applicable Norwegian VAT rate (usually 25%).
Understanding these calculations is essential to avoid overpayment or underpayment, which can result in penalties or audits.
How to correct errors in VAT returns in Norway?
Errors in VAT declarations must be corrected via an amended VAT return (MVA-melding) submitted to the Norwegian Tax Administration. Failure to correct errors in VAT reporting can lead to fines and additional audits, making it crucial for businesses to regularly review their filings.
Payment of VAT and customs duties
VAT and customs duties can be paid via:
- A customs credit account (Tollkreditt).
- Direct bank transfer to Norwegian Customs.
Businesses with high import volumes benefit from customs credit accounts, allowing them to pay in arrears rather than at the time of import.
VAT Refund on imports – Who can apply?
Businesses that are not registered for VAT in Norway may apply for a VAT refund if they meet the eligibility criteria. This requires submitting an application to Skatteetaten with supporting invoices. The refund process involves strict compliance with Norwegian VAT laws, requiring businesses to provide detailed records of transactions.
Special import procedures in Norway
Temporary importation rules
Temporary importation allows duty-free and VAT-free entry of goods under certain conditions (e.g., exhibitions, repairs).
A security deposit or guarantee may be required. These procedures are essential for companies involved in short-term business activities in Norway.
Free trade agreements and preferential tariffs in Norway
Norway has free trade agreements that reduce or eliminate customs duties for qualifying goods. Certificates of origin may be needed to benefit from lower tariffs. Companies importing from countries with trade agreements should ensure they have proper documentation to take advantage of these benefits.
Excise duties on specific goods
Certain goods (e.g., alcohol, tobacco, fuel) are subject to excise duties, which must be paid in addition to VAT and customs duties. Importers of these products should be aware of additional reporting requirements and regulations.
Alternative import schemes in Norway
VOEC Scheme for low-value goods
The VOEC (VAT on E-Commerce) scheme simplifies VAT collection for foreign sellers importing goods valued under NOK 3,000 to Norwegian consumers. Sellers must register with Skatteetaten to charge Norwegian VAT at the point of sale.
This scheme helps foreign e-commerce businesses comply with Norwegian VAT laws without requiring full VAT registration.
Handling dropshipping and e-commerce imports
Dropshipping businesses must comply with Norwegian VAT rules based on where the goods are shipped from and whether they use the VOEC scheme. Companies using dropshipping models should ensure they understand Norwegian tax implications to avoid legal issues.
Compliance and avoiding penalties in Norway
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect customs classification (HS codes – Harmonized System).
- Underreporting the value of goods.
- Failing to register for VAT when required.
Mistakes in VAT reporting can lead to fines and delays in processing goods. Regular compliance checks and professional assistance can help businesses avoid such errors.
Best Practices for Smooth Customs Clearance
- Use a trusted customs broker or automated declaration system.
- Ensure all documents are accurate and complete.
- Stay updated on changes to Norwegian VAT and customs rules.
Source: Imports in Norway
Zosia is a marketing specialist in Eurofiscalis, a company with a well-established position in the field of cross-border VAT compliance. Simultaneously, Zosia continues her academic development as a master’s student in Finance and Accounting, which enables her to stay up-to-date with evolving tax regulations.
Combining her knowledge of marketing with a deep understanding of finance and taxes, creates precise, substantive, and easily accessible content. Her mission is to educate in understanding the complexities of taxation related to doing business in international markets.
With her commitment, Zosia translates complex tax issues into clear language, providing valuable information that genuinely helps companies in their development and international expansion. She aims for tax information to be not only understandable but, above all, helpful in making business decisions.